Types of Survey: 20 Different Examples of Online Survey Method
Types of surveys encompass various methods for collecting information from individuals to understand their opinions, behaviors, and experiences. Email surveys, social media surveys, web-based surveys, and mobile surveys are typical examples of online survey methods. Face-to-face surveys involve survey interviews and intercept surveys. Telephone and SMS surveys collect responses through phone calls and text messages. Different types of surveys serve specific purposes, from measuring customer satisfaction to conducting market research and gathering demographic information. Explore the 20 different types of surveys, with a focus on online survey methods that are fast, efficient, and widely used. Each survey method requires specific question formats, distribution strategies, and technology platforms to ensure accurate and reliable data. Understanding different kinds of surveys and online survey formats enables researchers and organizations to choose the most effective approach for their research goals.
20 different types of surveys are listed below.
1. Survey Interview
A survey interview (in-person survey or household survey) is a research method where a researcher meets face-to-face with participants to ask questions and gather information. The survey interview format allows direct interaction between the researcher and the participant, creating opportunities for observation and deeper engagement compared to other survey methods.
Researchers use the survey interview method to collect detailed and personal feedback on sensitive or complex topics. The survey interview method allows for follow-up questions and probing to uncover more accurate and thorough responses. Skilled interviewers help participants feel comfortable, which encourages honest and genuine answers. Interviews enable researchers to observe tone, facial expressions, and body language, which provide additional insights into the truthfulness and meaning behind responses.
Examples of survey interviews include face-to-face conversations in a respondent’s home, interviews conducted at a public location such as a community center, or discussions recorded on camera for later review by experts to analyze verbal and non-verbal cues.
2. Intercept Surveys
An intercept survey (“man on the spot” survey) is a research method conducted at specific locations or events where interviewers approach passersby or attendees at random, to ask for their opinions or feedback on a topic. An intercept survey relies on the willingness of participants to participate immediately when approached.
Researchers use the intercept survey approach to capture spontaneous reactions and immediate impressions related to real-world experiences. The random selection of participants provides a diverse range of viewpoints, giving a snapshot of public sentiment.
Examples of intercept surveys include approaching shoppers in a mall to ask about their experience, questioning travelers at an airport about service quality, or asking event attendees for feedback right after a performance or activity.
3. Focus Groups Surveys
A focus group survey is a type of in-person survey that involves several participants instead of a single respondent. The group is small, demographically diverse, and guided by a trained moderator. New products are often tested, and specific topics, including controversial ones, are discussed during focus group surveys.
Researchers use the focus group survey format to gain detailed insights into participants’ attitudes and perceptions. The focus group survey format helps evaluate reactions to a product in a group setting and encourages interaction, discussion, and debate. The moderator observes and records participants’ behavior and viewpoints for analysis.
Examples of focus group surveys include assembling a diverse group to test a new food product, gathering participants to discuss political issues, or hosting sessions in multiple cities where attendees provide feedback on a proposed advertising campaign.
4. Panel Sampling Surveys
A panel sampling survey (panel survey) is a research method where a pre-recruited group of respondents maintained by a research company participates in multiple surveys over time. The panel sampling survey approach helps track changes and conduct longitudinal studies, providing access to participants who have specifically signed up to take part in them.
Researchers use the panel sampling survey technique to ensure a reliable pool of respondents and to target specific audiences by filtering participants based on chosen criteria. The panel sampling survey technique allows consistent data collection over time for analyzing trends and changes.
Examples of panel sampling surveys include tracking customer satisfaction over months with the same participants, monitoring consumer behavior changes for a product category, or studying public opinion shifts on social issues with a consistent respondent panel .
5. Telephone Surveys
A telephone survey (phone survey) is a research method conducted through Random Digit Dialing (RDD) to reach listed and unlisted numbers, improving sampling accuracy. Interviewers use Computer-Assisted Telephone Interviewing (CATI) software to perform the surveys, with telephone surveys displaying questionnaires to the interviewer and rotating questions for variety.
Researchers use the telephone survey approach to gather information from a broad audience efficiently when aiming for a geographically diverse sample. The telephone survey approach became popular in the mid-20th century when telephones were common in households, although its use has declined due to lower response rates.
Examples of telephone surveys include calling households to collect political opinion data, contacting customers to assess satisfaction with a recent service, or reaching out to residents to gather feedback on community projects or local government initiatives.
6. Post-Call Surveys
A post-call survey is a type of telephone survey conducted after a customer service call. After-call survey uses interactive voice response (IVR), where no interviewer is involved. Customers answer pre-recorded questions in post-call surveys by pressing numbers on their phone keypad or by speaking, with the system recording their responses.
Organizations use the post-call survey method to measure customer satisfaction and gather detailed feedback about recent service interactions. The post-call survey method helps evaluate the impression of the brand and the performance of specific service agents or contact centers.
Examples of post-call surveys include asking a bank customer to rate their experience, using a Net Promoter Score (NPS) survey to measure brand loyalty, or conducting a Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) survey to assess the outcome of a customer support call.
7. SMS Text Surveys
An SMS text survey is an interview form delivered through text messages to recipients who have agreed to receive notifications from the sender. Respondents answer directly from their mobile devices, making the process fast and convenient. Questions are short, and answers are limited to a few words or numbers in SMS text surveys, which is why they are used for Net Promoter Score (NPS) surveys.
Organizations use the SMS text survey method to quickly collect feedback, confirm appointments, or perform simple checks from younger or mobile-first audiences. The mobile text survey increases engagement and response rates while allowing automated follow-ups to encourage participation.
Examples of SMS text surveys include sending customers a one-question NPS survey after a purchase, asking patients to confirm an appointment with a short reply, or requesting residents to answer a quick public health check via text.
8. Postal Surveys
Postal Surveys are paper questionnaires sent directly to a recipient’s home address. Postal surveys gained popularity before the internet became widespread, mainly when participants lived far apart and survey budgets were small. A tangible and personal approach is achieved by including the recipient’s name and address on the envelope, creating a strong sense of direct connection in postal surveys.
The main goal of Postal Surveys is to reach target participants who have limited or no internet access, and groups that are difficult to contact through online methods. Printed surveys are used when a longer format is required, giving recipients the flexibility to complete them at their own pace. The personalized delivery increases the likelihood of the questionnaire being filled out and returned.
Examples of Postal Surveys include community feedback questionnaires sent to rural households, customer satisfaction forms mailed to recent product buyers, and public opinion polls delivered to voters in remote areas.
9. Kiosk Surveys
Kiosk Surveys are interactive questionnaires displayed on touch-screen stations in public locations. The kiosk survey stations are found in stores, hotel lobbies, hospitals, and office spaces, collecting feedback from customers or visitors. Immediate input is captured after a purchase or interaction, making responses more accurate in kiosk surveys.
The main goal of Kiosk Surveys is to gather real-time feedback while the experience is still fresh in the respondent’s mind. Businesses use them to track service quality, monitor compliance, or evaluate specific areas such as facility cleanliness. Customization for languages, customer segments, or available services increases the relevance of collected responses.
Examples of Kiosk Surveys include rating service quality at a fast-food restaurant checkout, assessing patient satisfaction in a hospital waiting room, and collecting visitor opinions about cleanliness in a shopping mall.
10. Email Surveys
Email Surveys are online questionnaires delivered directly to a recipient’s email inbox. E-surveys are easy to create and send using digital tools, allowing for personalization and audience targeting. Response tracking and performance analysis (open rates and A/B testing) are common features in email surveys.
The main goal of Email Surveys is to reach an identified audience for timely and targeted feedback. Businesses use email questionnaires for Business-to-Business (B2B) and Business-to-Consumer (B2C) engagement, integrating them with Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems to trigger surveys after specific actions (purchases or customer support interactions). Personalization using customer data improves response rates and feedback quality.
Examples of Email Surveys include sending a satisfaction questionnaire to clients after a service appointment, conducting market research with an existing customer list, and gathering employee feedback through a company-wide email campaign.
11. Pop-up Surveys
Pop-up Surveys are feedback forms that appear directly on a website or mobile app while a user is browsing. Website feedback forms temporarily block or overlay the content until the user responds or closes them. Placement within a site visit allows pop-up surveys to capture immediate impressions from visitors.
The main goal of Pop-up Surveys is to collect quick, real-time opinions from users as they interact with a digital platform. Companies use on-screen surveys to gauge user satisfaction, identify usability issues, and gather insights about specific products or content.
Examples of Pop-up Surveys include asking visitors to rate a shopping experience during checkout, gathering opinions on an article’s helpfulness, and requesting quick feedback after a live chat support session.
12. Embedded Surveys
Embedded Surveys are questionnaires placed directly on a website or digital platform. On-page surveys remain visible at all times, giving users constant access without pop-ups interrupting the experience. Continuous feedback collection is possible with embedded surveys, allowing ongoing insights from site visitors.
The main goal of Embedded Surveys is to gather consistent and long-term feedback from users while they interact with the website. Organizations use site-embedded questionnaires for course evaluations, product feedback, or usability studies. Visual integration into the site and incentives improve response rates and engagement.
Examples of Embedded Surveys include course feedback forms on university portals, product evaluation forms on e-commerce sites, and usability assessments embedded in software dashboards.
14. Mobile Surveys
Mobile Surveys are surveys tailored to display and function smoothly on smartphones and tablets. Smartphone surveys automatically adjust layouts and elements to fit different screen sizes. Researchers reach respondents wherever they are, providing convenient access on the go through mobile surveys.
The main goal of Mobile Surveys is to increase accessibility and flexibility for participants using mobile devices. Organizations use digital mobile polls to collect real-time feedback, conduct market research, or monitor user experiences without device limitations.
Examples of Mobile Surveys include customer satisfaction polls accessed on a smartphone, market research questionnaires completed on tablets, and event feedback forms sent via mobile links.
15. Mobile App Surveys
Mobile App Surveys are surveys conducted within a company’s mobile application. Users have already downloaded the app, showing a level of engagement that increases response likelihood. Contextual feedback is captured from users based on specific app actions or experiences in mobile app surveys.
The main goal of Mobile App Surveys is to assess customer satisfaction, track feature usage, and identify areas for improvement. Organizations use in-app surveys to collect insights post-purchase, after feature use, or before app uninstallation, integrating analytics for deeper analysis.
Examples of Mobile App Surveys include in-app feedback after a purchase, satisfaction ratings following a new feature release, and exit surveys when users attempt to uninstall the app.
16. QR Code Surveys
QR Code Surveys are surveys accessed by scanning a Quick Response (QR) code with a mobile device. The QR code directs respondents to a survey, making the process quick and convenient. The QR code directs participants to a survey, simplifying access and completion in QR Code Surveys.
The main goal of QR Code Surveys is to make survey participation effortless and immediate. Organizations use scan-to-survey forms to collect feedback at physical locations, promotional events, or advertising campaigns, allowing fast and easy response capture.
Examples of QR Code Surveys include feedback forms on restaurant receipts, customer satisfaction surveys on product packaging, and event opinion polls on posters or flyers.
17. Delphi Surveys
Delphi Surveys are structured questionnaires to gather expert opinions on specific topics. Experts provide their insights anonymously through multiple rounds of feedback. Consensus is refined over time, making Delphi Surveys effective for complex problem-solving and forecasting.
The main goal of Delphi Surveys is to collect informed judgments from specialists while avoiding bias or group influence. Researchers use Delphi method studies for decision-making in uncertain or evolving fields, such as healthcare, technology forecasting, and policy development, where collective expert insights are critical.
Examples of Delphi Surveys include predicting future healthcare trends, developing technology adoption roadmaps, and shaping public policy initiatives through expert consensus.
18. AI Surveys
AI Surveys are surveys conducted using artificial intelligence (AI) systems that ask questions and adapt in real time. The AI follows up automatically based on previous responses, improving the depth and relevance of feedback. The technology adapts questions in real time, allowing dynamic, interactive data collection in AI Surveys.
The main goal of AI Surveys is to gain deeper insights into customer motivations, experiences, and preferences through automated, adaptive questioning. Organizations use automated surveys to understand behavior patterns, test product concepts, or analyze market trends with high efficiency.
Examples of AI Surveys include chatbot-driven customer satisfaction surveys, adaptive product feedback forms, and automated market research questionnaires that adjust based on prior answers.
19. Web-based Surveys
Web-based surveys are digital questionnaires completed through internet platforms, websites, or email links. Respondents access and fill out survey forms using computers, tablets, or mobile devices, making data collection fast, scalable, and cost-effective in web-based surveys.
The main purpose of web-based surveys is to gather quantitative and qualitative information from target populations for research, feedback, or decision-making. Organizations use online surveys to measure opinions, behaviors, satisfaction levels, and demographics without the limitations of paper-based methods.
Examples of web-based surveys include customer satisfaction surveys after online purchases, employee engagement forms on intranets, academic questionnaires on university sites, product feedback on e-commerce platforms, political polls, event feedback forms, and patient health screening questionnaires.
20. Market Research Surveys
Market research surveys are structured tools to collect information on consumer preferences, market trends, brand perception, and purchasing behaviors. Marketing Surveys focus on specific demographics or market segments, making insights from market research surveys highly targeted and actionable.
The purpose of market research surveys is to provide actionable insights that guide business strategies and reduce market risks. Customer feedback surveys help companies evaluate consumer demand, test new products, measure brand awareness, and understand competitive advantages.
Examples of market research surveys include brand awareness surveys assessing logo recognition, product concept testing questionnaires, price sensitivity studies, competitor analysis surveys, market segmentation research, purchase intention surveys, usage and attitude studies, and mystery shopper surveys evaluating retail customer service.
Online Surveys: Ideal for Collecting Data and Feedback
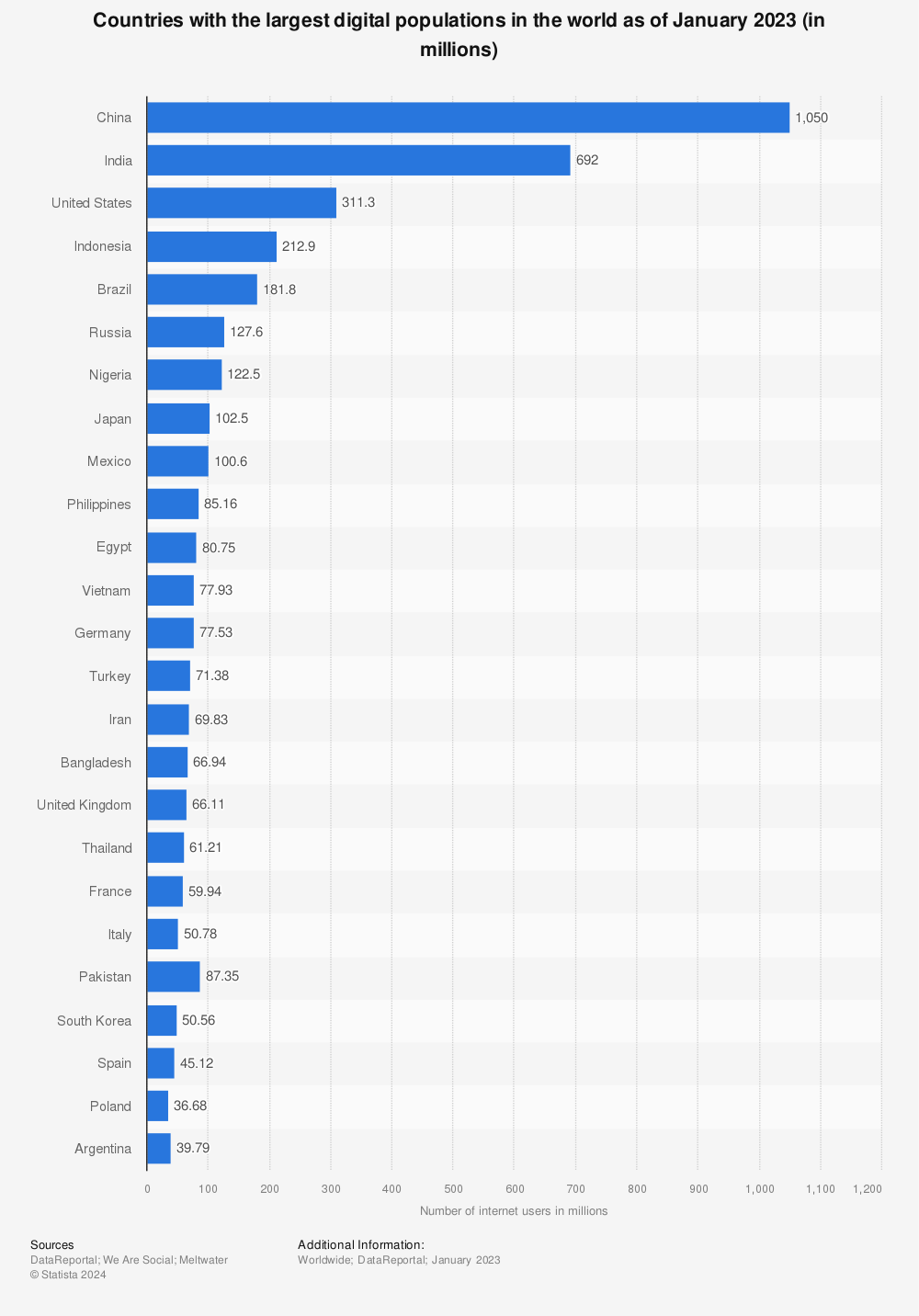
While other options exist, the majority of surveys today are conducted online in one form or another. Online surveys are generally the best way to collect data and feedback, as internet usage, across most countries, is incredibly high! Here’s a look at how many people are using the internet by country. And remember, this is in millions!
The data collected from online surveys can vary depending on the type of survey, the sample size, and the target population. Online surveys often include demographic questions to better understand respondents and use rating scales for quantifiable feedback. They are suitable for both descriptive research and trend analysis, including trend surveys and cohort surveys, which help track changes in opinions or behaviors over time. Online surveys can collect both quantitative and qualitative data, and qualitative feedback and qualitative insights are valuable for understanding customer motivations and experiences.
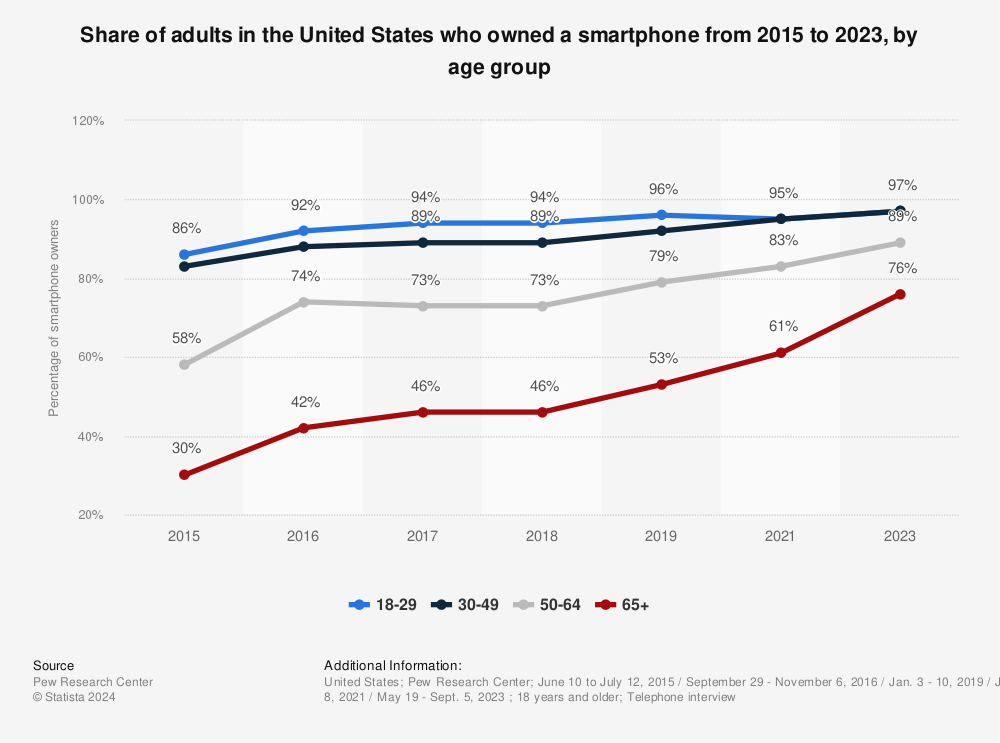
At one time, there was concern that online surveys had an age bias. However, today there is a much better balance between age groups using the internet. According to Pew Research, the share of adults in the United States using the internet are as follows:
That’s not all. People can take online surveys just about anywhere thanks to mobile devices. The use of these devices across age groups is balancing out as well. Check out smartphone use by age group below.
With more and more people accessing the internet through their mobile devices, now you can reach teens while they’re between classes and adults during their subway commute to work. Can’t say that for those other types of surveys!
Online surveys are also extremely cost-efficient. You don’t have to spend money on paper, printing, postage, or an interviewer. This significantly reduces set-up and administration costs. This also allows researchers and companies to send out a survey very expeditiously. Additionally, many online survey tools provide in-depth analysis of survey data. This saves you from having to spend money on further research once the survey is complete.
Create your first survey, form, or poll now!
Conclusion
Researchers have their pick of options when it’s time to conduct research and survey people. Which method you choose may depend upon cost, reach, and the types of questions.
Now, you may be wondering, “Where can I make free surveys?” You can get started with free online surveys using SurveyLegend! Here are a few things that make SurveyLegend the ideal choice for different types of surveys for research (or for fun).
- When it comes to surveys, making it brief is best to keep respondents’ attention. So, SurveyLegend automatically collects some data, such as the participant’s location, reducing the number of questions you have to ask.
- People like eye candy, and many surveys are just plain dull. SurveyLegend offers beautifully rendered pre-designed surveys that will get your participants’ attention – and keep it through to completion!
- Today, most people take surveys on mobile devices. Often surveys desktop surveys don’t translate well, resulting in a high drop-off rate. SurveyLegend’s designs are responsive, automatically adjusting to any screen size.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
An online survey is a digital questionnaire that organizations, businesses, and researchers send over the internet to collect information from participants. The web-based forms allow respondents to answer questions using computers, smartphones, or tablets from any location with internet access. Companies use online surveys to gather feedback after purchases, restaurants collect opinions about food and service, schools ask parents about policies, and healthcare providers assess patient satisfaction. The convenience of an online survey makes it an effective tool for data collection, allowing participants to complete questions at their own pace while organizations automatically compile and analyze responses for faster, more accurate insights.
The key elements that make a good survey questionnaire for market research are listed below.
- Clear, Unbiased Questions: Questions are written neutrally to avoid leading respondents toward specific answers in a survey questionnaire.
- Concise and Straightforward Language: Everyday words are used so participants understand without confusion in the questionnaire method of data collection.
- Logical Question Order: Questions progress from general to specific, creating a natural flow in an online questionnaire.
- Relevant Questions to the Research Objective: Each question directly addresses the research goals in the Survey Questionnaire.
- Balanced Response Options: Positive, negative, and neutral choices are provided equally.
- Avoidance of Leading or Loaded Questions: Questions do not assume or imply a specific answer.
- Appropriate Question Types (Multiple Choice, Rating Scales, Open-ended): Various formats are used to collect quantitative and qualitative insights.
- Consistent Formatting and Style: Fonts, layouts, and question designs remain uniform throughout the survey.
- Pilot Testing Before Full Distribution: Surveys are tested on a small audience to identify issues before full deployment.
- Anonymity and Confidentiality Assurance: Respondents are assured that their answers are private and are not traced back to them.
The common uses of internet surveys for gathering feedback are listed below.
- Customer Satisfaction Surveys: Restaurants collect feedback after dining experiences using internet surveys to measure food quality, service, and overall satisfaction. Hotels use online surveys following guest stays to evaluate room cleanliness and staff friendliness. Retail stores gather opinions about shopping experiences, product availability, and checkout processes through digital surveys.
- Product Feedback Collection: Technology companies distribute internet surveys to users after product launches to gather opinions on features and performance. Automotive manufacturers collect feedback about vehicle reliability, comfort, and desired improvements using online surveys. Software companies use electronic surveys to understand user experiences and identify necessary updates.
- Employee Engagement Surveys: Large corporations conduct internet surveys annually to measure workplace happiness, management effectiveness, and career growth opportunities. Healthcare systems evaluate work conditions, training needs, and job satisfaction through staff online surveys. Retail chains like Walmart assess workplace culture, benefits satisfaction, and communication effectiveness using web surveys.
- Market Research Studies: Consumer goods companies use internet surveys to test new product concepts before launch. Fashion retailers collect customer opinions about trending styles and popular colors using online surveys. Food companies gather feedback on recipe changes and new flavor options through digital surveys.
- Event Feedback Assessment: Conference organizers send internet surveys to attendees to evaluate speaker quality, venue satisfaction, and content relevance for planning improvements. Wedding venues gather bride and groom feedback about service quality and experience via online surveys. Concert venues collect audience opinions about sound quality, seating comfort, and facility cleanliness using e-surveys.
- Educational Program Evaluation: Universities send internet surveys to students to assess professor effectiveness, curriculum quality, and learning resources. Online websites collect completion feedback about course content, video quality, and assignment difficulty through web-based surveys. Training companies use online surveys to evaluate course effectiveness and identify areas for improvement.
To earn money from online surveys, there are five steps to follow. First, sign up with reputable paid survey websites (Swagbucks, Survey Junkie, or InboxDollars) that reward users for completing questionnaires. The survey websites provide access to market research online surveys from companies seeking consumer feedback. Second, fill out profile information accurately to ensure survey invitations match demographic requirements (age, location, or interests). Third, check emails frequently for survey invitations and respond promptly since slots for popular surveys fill quickly. Fourth, answer questions honestly and carefully to maintain good standing with survey platforms and qualify for additional opportunities. Fifth, accumulate points or cash rewards by completing surveys consistently, as platforms require minimum thresholds before withdrawals. Longer online survey market research studies (surveys focused on healthcare or technology products) offer higher rewards, allowing dedicated participants to earn a steady supplemental income over time.
An Online Survey differs from the face-to-face survey method by offering lower costs, greater anonymity, and faster data collection. Face-to-face surveys provide richer, qualitative insights. Online surveys are conducted digitally, allowing participants to answer questions privately on computers, tablets, or smartphones. Respondents feel more comfortable sharing honest opinions about sensitive topics (personal finances or health) because online surveys protect their identities. The online surveys reach large audiences quickly and require minimal resources, making them less expensive than a face-to-face survey method that involves interviewer training, travel, and hourly wages.
Face-to-face surveys use trained interviewers to engage directly with participants, ask follow-up questions, clarify confusing answers, and observe non-verbal cues like body language or facial expressions. The face-to-face survey method enables researchers to gather detailed explanations and explore the reasoning behind responses, producing in-depth qualitative feedback. Interviews last 30 to 60 minutes. Online surveys take 5 to 15 minutes and focus primarily on quantitative data. Response rates differ, with face-to-face surveys achieving higher completion rates due to personal interaction. Online surveys have lower participation because recipients ignore digital invitations.
A digital survey gathers data through automated electronic systems compared to paper surveys, which depend on manual distribution and collection. Digital surveys store participant responses directly in electronic databases as respondents complete questions online, eliminating the need for data entry by staff. Paper surveys require printed questionnaires to be handed out or mailed, collected physically, and manually entered into computer systems for analysis. Digital surveys reach participants instantly via email links, website forms, or mobile devices. Paper surveys require printing, mailing, or hand delivery, adding weeks or months to the research process.
Data accuracy differs notably between the digital and paper surveys. Digital surveys include built-in validation features that prevent errors. Digital forms require mandatory answers for each question and automatically reject invalid entries, such as text in numeric fields. Paper surveys allow skipped questions, illegible handwriting, or multiple selections where only one is allowed. Digital surveys remove transcription mistakes that occur when staff manually enter handwritten responses.
Cost and convenience set the digital and paper surveys apart. Digital surveys reduce expenses by eliminating printing, postage, and labor costs for manual processing. Paper surveys require substantial upfront investments for materials, mailing, and staff time. Survey participants complete digital surveys immediately on computers, tablets, or smartphones from any location with internet access. Paper surveys demand access to writing materials, physical completion, and remembering to return forms. Digital surveys provide real-time tracking of responses, enabling reminders for non-participants. Paper surveys offer no visibility into response progress until forms are physically collected.
The advantages of online surveys are listed below.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Online surveys eliminate printing costs, postage fees, and paper expenses required for traditional mail surveys. Researchers save money by avoiding interviewer wages, travel expenses, and venue rental fees linked to face-to-face data collection. Digital questionnaires tend to reach 1,000 survey participants for a fraction of the cost of paper-based studies, demonstrating one of the key benefits of online surveys.
- Speed of Data Collection: Digital surveys gather responses within hours or days, rather than the weeks or months needed for traditional methods. Participants receive invitations instantly through email and complete questionnaires immediately on their devices. Automated systems process responses in real-time, allowing researchers to view results as they are submitted.
- Large Reach and Accessibility: Online surveys reach participants across countries, states, and cities without the geographical limitations of traditional surveys. Respondents complete questionnaires from home, work, or any location with internet access using smartphones, tablets, or computers. Digital distribution allows thousands of participants to provide feedback simultaneously.
- Ease of Data Analysis: Responses automatically transfer into spreadsheets and databases, eliminating manual entry errors and delays. Statistical software imports survey data directly for immediate processing, calculations, and visualization creation. Researchers generate charts, graphs, and reports quickly, making it a key benefit of online surveys.
- Participant Anonymity and Honesty: Online surveys provide privacy since participants answer questions without revealing identities. Anonymity encourages honest feedback on sensitive topics (income, health conditions, or controversial opinions), improving the reliability of responses.
- Environmental Benefits: Digital surveys reduce paper waste, printing materials, and transportation emissions compared to traditional surveys. Electronic questionnaires avoid thousands of printed pages and fuel consumption, supporting sustainability while maintaining effective data collection.
- Real-Time Monitoring and Flexibility: Researchers track response rates, completion percentages, and participant progress instantly through online dashboards. Survey administrators adjust questions, extend deadlines, or send reminders without reprinting materials. The adaptability of online platforms is one of the significant advantages of online surveys for dynamic research needs.
Electronic surveys help in gathering large amounts of data quickly by using digital distribution systems to reach thousands of survey participants simultaneously through email, social media, or website links. Responses are stored automatically in databases as participants complete questionnaires, removing the manual entry and processing steps required by paper surveys.
Electronic surveys allow participants to answer questions instantly on smartphones, tablets, or computers from any location with internet access. Built-in validation checks ensure responses are complete and correctly formatted. Automated reminders increase participation rates. Data exports occur immediately in formats (spreadsheets or statistical software files), allowing researchers to analyze results and share insights with team members without delays.

13. Social Media Surveys
Social Media Surveys are polls and questionnaires distributed through social media platforms such as Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, and Threads. Online social polls leverage high user engagement and allow companies to reach millions of users in real time. Quick feedback collection and public opinion monitoring are possible through social media surveys.
The main goal of Social Media Surveys is to measure customer sentiment and track brand perception among online audiences. Companies use social media polls to segment by age, location, interests, and engagement levels for targeted insights. Fast, viral sharing increases participation and awareness.
Examples of Social Media Surveys include Instagram polls for product preferences, Twitter surveys on service satisfaction, and Facebook forms measuring event or campaign feedback.