A high response rate is important to anyone conducting a survey. However, when surveys ask respondents irrelevant questions – or questions that don’t make sense based upon a respondent’s previous answers – many people will get frustrated and drop out. That’s why it’s important to create smart skip logic surveys and brand logic surveys. In this blog, we’ll take a look at how this helps create intuitive surveys that participants enjoy taking.
Create your survey with logic flows now!
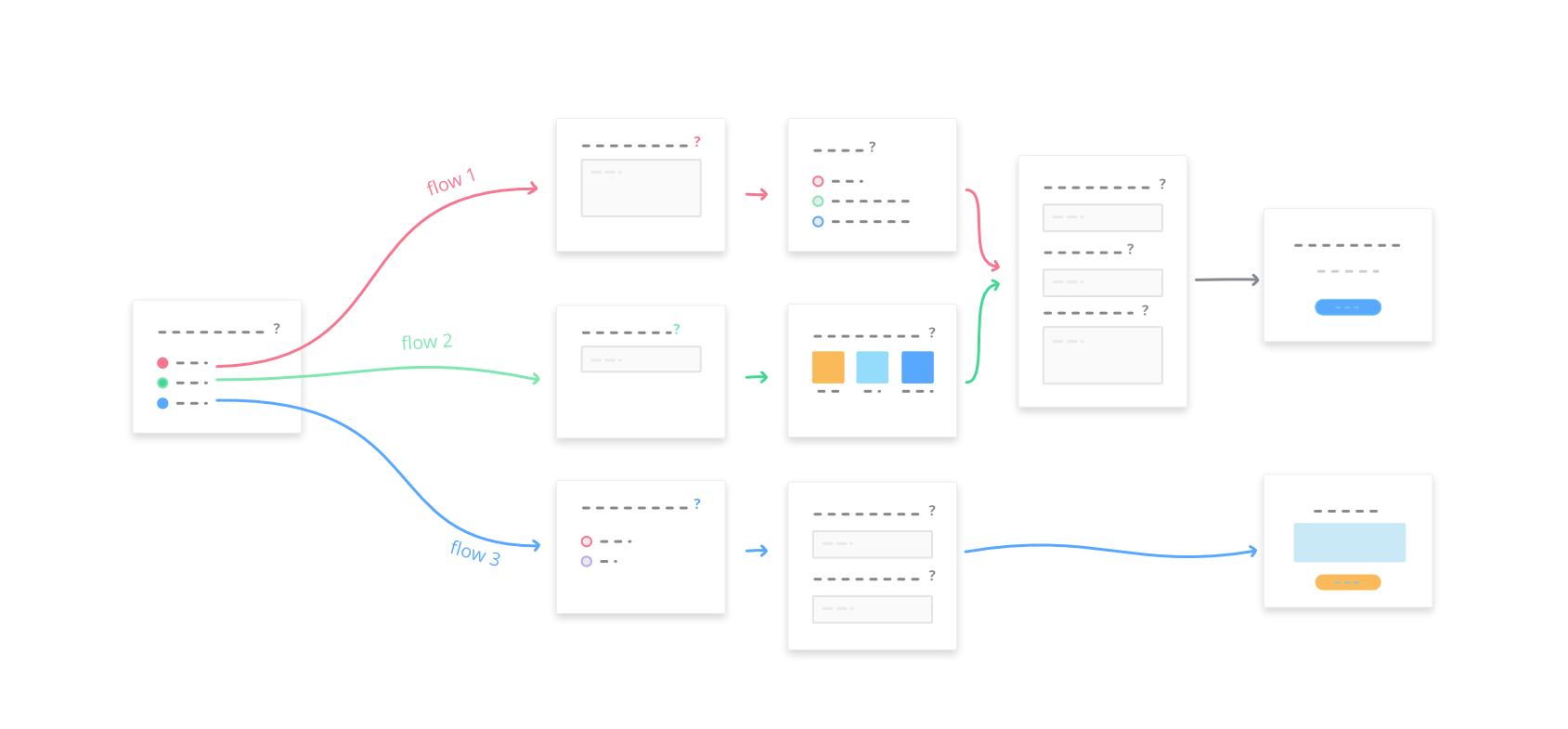
What is Survey Logic?
In the study of logic, researchers look at the rules and techniques that allow people to distinguish good, correct reasoning from bad, incorrect reasoning. This also applies to the survey world. Survey logic is what allows you to create a survey that flows based on the answers of respondents. Based on their answers, only relevant questions are asked of them. So, let’s take a look at some examples of survey logic.
Survey Logic Examples
- Let’s say you’re conducting a survey on political voting. If a person answers that they regularly vote, you may want to skip certain questions and keep the survey short. If they answer that they rarely or never vote, you may want to ask more questions. This will help you understand how you can convince these people to be more active in the voting process.
- Now, suppose you are emailing a survey about health that includes gender-specific questions. Using survey logic, you can design a logic flow that automatically hides questions that are relevant to males when respondents are female and vice versa.
- How about employee satisfaction surveys? The experience of each employee is different, so you want to be able to customize their survey path based on the answers they provide. Skip logic surveys can help present the right questions to the respondents.
- For our last example, consider a restaurant satisfaction survey asking if the respondent enjoyed their experience. If they answer “yes,” you may simply jump to a follow-up question about what they enjoyed most and then thank them for their time. If the answer is no, you may want to jump to a series of questions asking about food quality, service, cleanliness, pricing, staff, and so on to better understand what they didn’t like about their experience.
This is how survey logic helps you design better surveys.
5 Reasons to Use Survey Logic
As you can see, survey logic simply presents a better, more thoughtfully designed survey to participants. But there are other benefits as well.
1. More Engaged Participants
When survey takers notice that the survey is “smart” – only asking relevant questions based on previous answers – they’ll become more engaged and more likely to follow the survey to completion. If your survey is shareable, they may even share it on social media increasing your survey’s reach.
2. Shorter Surveys/Completion Time
People no longer have patience for long surveys, giving rise to short surveys, also known as “micro surveys.” With survey logic, you can shorten your surveys by having respondents jump to relevant questions only, reducing the time they need to spend taking the survey.
3. Less Need for Incentives
Survey incentives (cash, gift cards, discounts) can get costly but are sometimes a necessity when surveys are long. Shortening a survey with survey logic requires less of a time commitment from respondents. That commitment means they’re less likely to expect an incentive.
4. Lower Survey Dropout Rates
When questions are not relevant to the participant or ask a contradictory question based on how they’ve responded to previous questions, they’re likely to become annoyed and drop out of the survey. For example, if they state that they do not like sports, and the next question asks what their favorite sport is, they may just exit the survey in frustration.
5. Higher Quality Data
Increased rates of survey completion increase the amount of data you collect as well as its accuracy. Respondents are also more engaged with shorter, relevant surveys, and are likely to be more thoughtful about their responses rather than flying through the survey, also improving data accuracy.
Survey Skip Logic and Skip Branching with SurveyLegend
As highlighted, skip logic is used to let survey respondents skip one or more questions, jumping to a different question, page, or survey. Branch logic executes this based on how a participant responds to a question. Your survey can be designed to define rules to create a custom path for each respondent, depending on the answer to a specific question. Branching questions create “intelligent” surveys, i.e., respondents can answer only those questions that apply to them based on their responses to screening questions.
SurveyLegend empowers you to easily create powerful and very advanced survey logic flows. You can combine several logic rules, and ask our system to perform several actions and consequences based on respondents’ answers, geo-location, and other information.
Please note that there are many online survey solutions using logic terms interchangeably, e.g. question logic, skip logic, branching, piping, survey rules, form rules, and so on. To simplify, we call it them “Logic Flows.” With our “Logic Flows” not only you can do everything that other survey tools offer under different names, but also you can go beyond that and enjoy creating smart surveys with pictures!
Example of Logic Flows with SurveyLegend
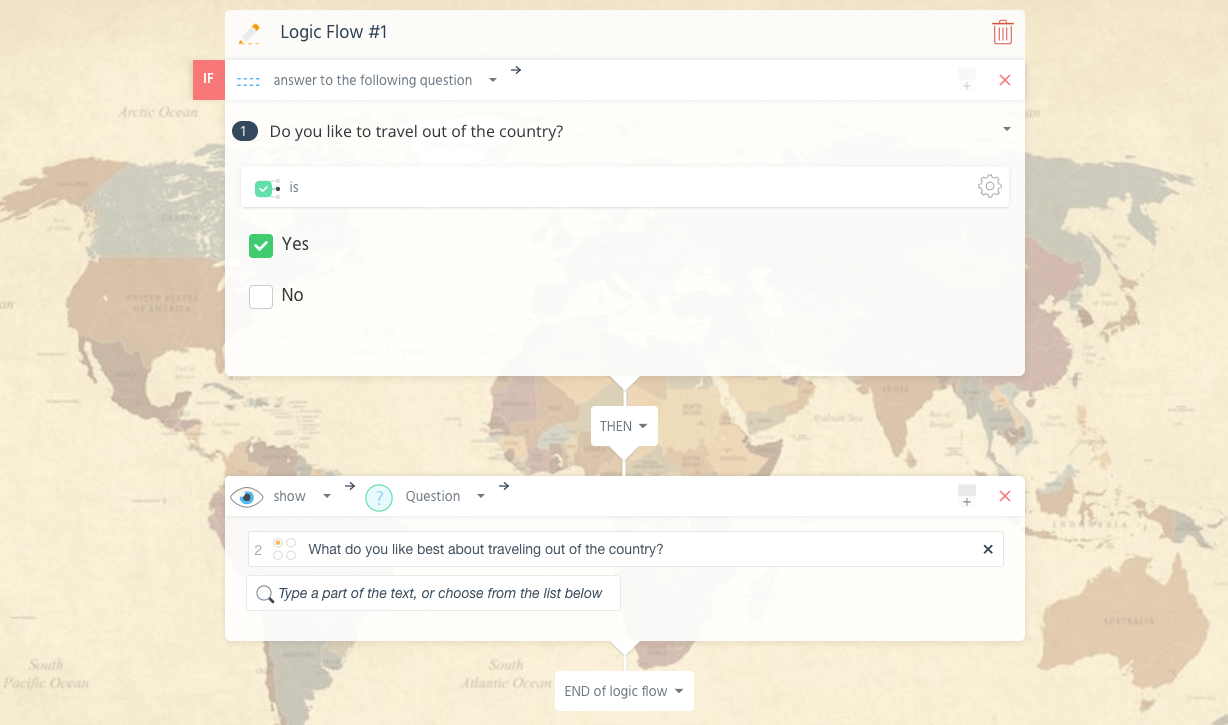
Here is a look at how a basic “IF/THEN” survey flow works using the SurveyLegend survey tool. As you become more familiar with the survey creation tool, you can increase the complexity of your logic flows to create extremely smart surveys!
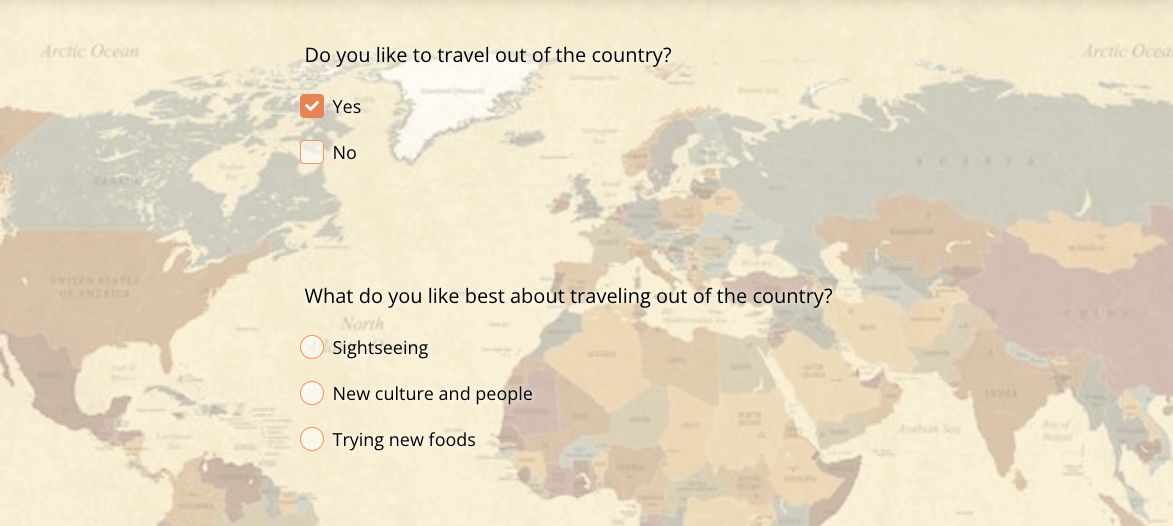
Below is a logic flow centering on traveling. If a respondent says they like to travel, an “IF YES, THEN” rule applies:
The respondent sees only the following:
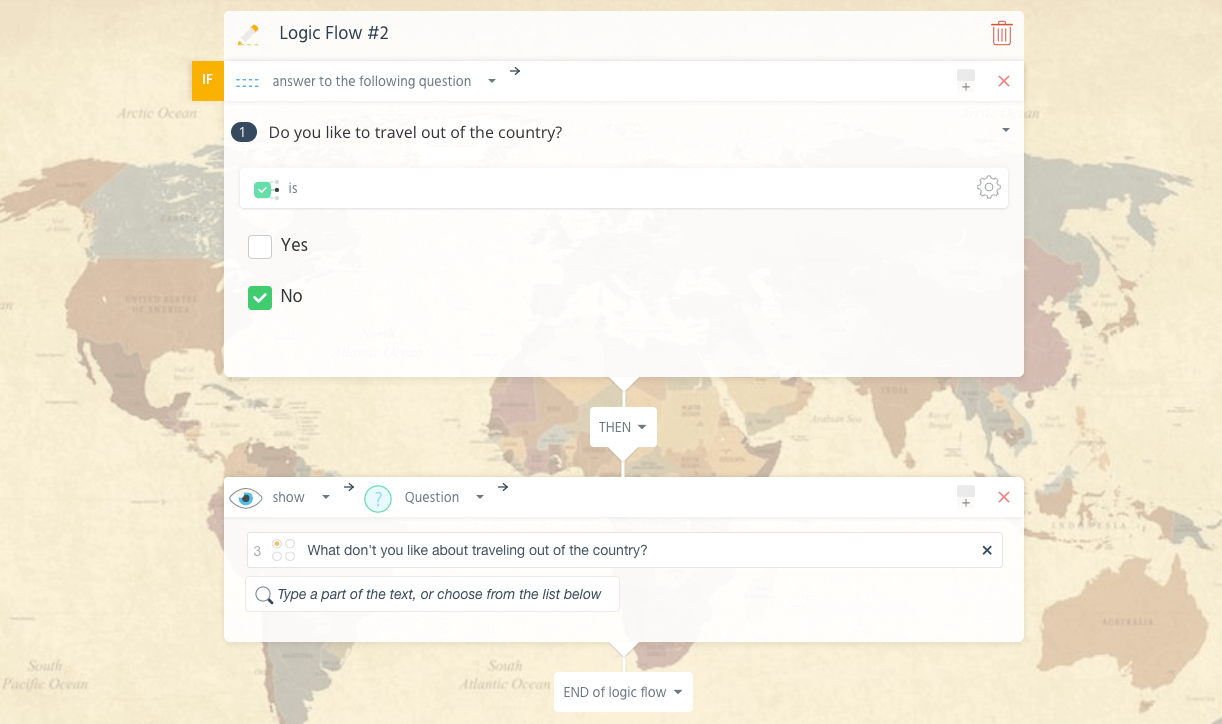
Now, if the respondent says they do not like traveling, an “IF NO, THEN” rule applies:
The respondent sees only the following:
Check out more great content and user information on surveyLegend logic flows!
- Survey Logic User Guide
- Logic Flow User Guide
- How to Use Skip Logic Questions
- How to Use Branch Logic Questions
Conclusion
Because of the ease of sending online surveys, people are being solicited to participate in them more often. Unfortunately, this can lead to survey fatigue. So, it’s important to make your surveys as smart and engaging as possible. This can be easily accomplished using logic flows with SurveyLegend. By implementing logic flows into your surveys, forms, or questionnaires, you can create smart surveys that intelligently react to respondents’ answers, and trigger a different consequence. You can even make an advanced logic flow that has several rules and performs multiple actions. In the end, you’ll have more engaged respondents, more accurate responses, and better quality data! Get started with SurveyLegend’s free online survey with skip logic today!
Create your survey with logic flows now!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Survey logic allows online survey designers to create a smart survey that flows based on the answers of respondents. So, depending on their responses, only relevant questions appear next while other questions are skipped and the respondent never sees them.
Skip logic is a feature on some online surveys that enables survey designers to give respondents a unique and personalized experience. This is dependent on their answers throughout the entire survey. It’s like automatically generating a unique questionnaire for each respondent. Learn more about skip logic.
Branch logic, or “branching,” lets you customize the behavior of your survey, form, poll, or questionnaire based on multiple conditions. With branching, you can forward respondents who answer a series of questions in a certain way to a different section of the questionnaire, basically hiding the rest of it. Learn more about branch logic.